OEE Power in Smart Factory
An Advanced Guide on How to Calculate OEE
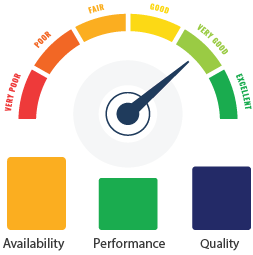
Understanding OEE
Availability

Performance

Quality


OEE Formulas to Calculate OEE Factors
Availability – Maximizing uptime for efficiency

Planned Production Time
This is the total time that the equipment is scheduled to be available for production. It represents the maximum possible time the equipment could be operating if there were no interruptions.Actual Production Time
This is the actual time the equipment is producing goods, after subtracting any downtime due to planned maintenance and unplanned stops.Performance – Tuning speed and quality

Actual Output
It is the sum of all the parts resulting from production (it can also be a volume or batches) and includes any type of production result (parts or volume: good, bad and under quality review).Theoretical output
It is the expected production based on the actual production time divided by the ideal cycle time. This calculation helps determine the expected number of units produced during the productive time. The formula is as follows:Ideal Cycle Time
The ideal cycle time, also known as the design cycle time, is generally considered to be the theoretical minimum time to produce a part defined as the design of the equipment. The inverse of the ideal execution rate. It is used to calculate OEE performance. A variation of the calculation uses the ideal execution speed instead.Actual Production Time
Its considered as the current production time is the sum of all the production times recorded by a piece of equipment, i.e. the sum of all the production periods or processes executed.Quality – Ensuring promised standards

OEE calculation – A step-by-step guide
- Formula: Availability = (Actual Production Time / Potential Production Time) * 100%
- Potential Production Time: 10 hours or 600 minutes
- Planned Stops: 3 x 20 minutes, totaling 60 minutes
- Unplanned Stops: 70 minutes
- Actual Production Time = Potential Production Time − Planned Stops − Unplanned Stops
- Production Planned Time: 600 minutes – 60 minutes – 70 minutes = 470 minutes
- Availability = (Actual/ Production Time / Potential Production Time) * 100%
- Availability = (470 minutes / 600 minutes) * 100%
- Availability = 78.33%
- Formula: Performance = (Actual Output / Theoretical Output) * 100%
For example, suppose a manufacturing machine has an Ideal Cycle Time of 20 seconds, allowing it to produce 3 units per minute. Over a production period of 240 minutes, the actual production time, the machine successfully manufactures 650 units.
Here are the variables:
- Ideal Cycle Time: 20 seconds
- Actual Production Time: 240 minutes
- Actual Output: 650 units
To calculate Theoretical Output:
- Theoretical Output = Actual Production Time / Ideal Cycle Time
- Theoretical Output = 240 minutes * 60 seconds / 20 seconds per unit = 720 units
Now, to find Performance:
- Performance = (Actual Output / Theoretical Output) * 100%
- Performance = (650 units / 720 units) * 100%
- Performance = 90.28%
In this scenario, the performance of the manufacturing machine is approximately 90.28%.
- Formula: Quality = (Good Unit Output / Total Output) * 100%
For example, during a production shift, a manufacturing line produces a total of 620 units. After inspection, it was found that 30 units were defective and declared as rejects.
From this information, we can identify:
- Total Output during the shift: 650 units
- Good Unit Output: The actual number of good parts produced is 650 – 30, so 620 units
To calculate Quality:
- Quality = Good Unit Output / Total Output * 100%
- Quality = 620 units / 650 units * 100%
- Quality = 94.67%
So, the quality of production in this scenario is approximately 94.67%.
- Availability in decimal form: 0.7833
- Performance in decimal form: 0.9028
- Quality in decimal form: 0.9467
Using the calculations for Availability, Performance, and Quality, we know,
- OEE = Availability * Performance * Quality * 100%
- OEE = 0.7833 * 0.9028 * 0.9467 * 100%
- OEE = 66.70%
What Do The Results Say?
The calculations using the formula for OEE provide results that indicate and shed light on different aspects of equipment performance and production quality. A higher OEE percentage signifies better overall equipment effectiveness. It showcases that the equipment operates efficiently, with minimal downtime, optimal speed, and high-quality output.
The results and the interpretation vary in the context of industry standards and specific production goals. OEE can vary according to the equipment design, maintenance practices, and product complexity. You can analyze the calculation of OEE results over time and compare them to benchmarks. You can identify opportunities for improvement and implement strategies to enhance operational efficiency and productivity. Customizing the needs and wants of your industry is the finest way to achieve desirable results with the help of OEE.
Example AnalysisThe Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) in the examples used is Approximately 66.70%., The OEE Calculations step-by-step guide offers you valuable insights into understanding OEE. It allows you to identify areas for improvement, optimize production processes, and drive efficiency in your manufacturing operations. The knowledge comes in handy to make informed decisions to maximize productivity and achieve operational excellence.
In this example, the company has a significant gap from the target OEE. The most critical area of opportunity is availability, which is the lowest value and negatively impacts the OEE calculation. This low availability reduces the overall effectiveness, even though the other pillars (performance and quality) are above 90%, surpassing world-class industry targets.
Go from theory to action: try our interactive OEE calculator
Top Mistakes When Calculating OEE
Manual Data Collection
Use of manual data collection leads to insufficient or poor data results. Employees carrying out manual data collection tasks are often likely to miss readings, overlook relevant changes or read incorrect numbers. This manual data collection method leads to insufficient data for accurate OEE calculation.

Inaccurate Equipment Run Speed
You may find managers or supervisors in a manufacturing organization using scheduled or average equipment speed instead of the rated speed for OEE calculation. Using the planned equipment speed makes the OEE score to increase but it in reality it hides the improvement opportunities.

Paying Less Attention to all Production Stops
A manufacturing organization should be able to evaluate accurately between the planned and unplanned stops to calculate OEE effectively. Considering most of the stops as “planned” may lead them to miss opportunity for improvement. It’s important to acknowledge unplanned stop and try to find the root cause to avoid such stops in future.

Inconsistent OEE Calculation
Standardization is essential when calculating OEE across plants in different geographies. Consistent usage of data, methods, and approach ensures accurate OEE calculation and leads to effective communication across the organization. It’s always the best practice to centralize the data collection that different plants and machines can refer to.

Short Time Period for Calculation
Choosing a short time period such as a single day shift for OEE calculation leads to inaccurate results that should not form the basis for analysis and improvement. It is important to gather sufficient data over a longer period of time, such as a month or 3 months to take into account the productivity peaks and downtime.
OEE Data Collection- The Building Blocks
- Capture essential production data such as start and stop times, downtime events, production counts, and any relevant parameters specific to the equipment or process.
- Utilize real-time monitoring systems for continuous collection of data throughout the production process. It offers immediate detection of issues and empowers operators to take timely actions.
- Accurately tracking downtime events is critical for assessing equipment availability. It allows for proper log creation for log time and ensures nothing goes missing.
- Monitoring equipment performance involves tracking production rates, cycle times, and efficiency metrics. It allows for a quick detection of deviation from expected production rates.
- Collecting quality data involves tracking the number of acceptable and defective units produced during a given period. This data enables accurate OEE calculation and improves insights.
- Integrating data collection systems with OEE software platforms is effective. It automates data capture, consolidates information, and provides reports for performance monitoring and analysis.
Optimize Your Production Process With Our Production Module
OEE implementation strategies

Define Clear Objectives
Define the goals and objectives of implementing OEE within your organization. It includes reducing downtime and waste, increasing throughput and quality, and so on. Having clear objectives will guide your OEE implementation efforts.

Invest in Technology
Utilize advanced technology solutions such as OEE calculator software and real-time monitoring to collect, analyze, and visualize data.
They enable proactive decision-making and timely intervention to address issues.

Standardize Processes
Standardize operating procedures and maintenance practices to minimize variability and optimize equipment performance. It helps ensure consistency and reliability in production operations.

Provide Training and Education
Ensure that employees understand the concept of OEE and its importance in improving efficiency. Provide training sessions and educational materials to empower staff with overall equipment effectiveness formula and strategies.

Implement Lean Manufacturing Principles
Incorporate lean manufacturing principles to eliminate waste, reduce setup times, and improve overall equipment effectiveness. They complement OEE by fostering a culture of continuous progress and efficiency.

Set Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define key performance indicators aligned with OEE goals and regularly monitor progress. They provide valuable insights into equipment performance and help track improvements over time.

Encourage Cross-Functional Collaboration
Foster collaboration between different departments to identify root causes of inefficiencies. Cross-functional teams can leverage their expertise to drive OEE improvements holistically across the organization.

Constant Monitoring and Improvement
Implement a culture of continuous monitoring and improvement. Regularly review, analyze, and act on changes. Encourage feedback and conduct brainstorming sessions for OEE optimization.